
Introduction of Cyber Security
On the internet, data or information is widely spread and with each year, technology is becoming more comprehensive and complicated, and so do cyberattacks. Digital crime is also enhancing with great intensity and certainly, it is not restricted to any specific Internet-accessible platforms. Different devices such as desktops, smartphones, and tablets each might carry a particular level of digital defense, yet each device contains certain vulnerabilities which provide a pathway for hackers to attune to the devices.
On the positive side, particular digital security tools and services operate parallel to these negative tech counterparts.
In this section, we will emphasize on the introduction of cyber security and other associated concepts of the same. Cyber security refers to the set of techniques that are used to conserve the integrity of networks, programs, and data from attack, damage, or unauthorized access. Information technology includes a broader category that preserves all information assets, be it in hard copy or digital form. The term cyber security is not restricted to computers, but it is also implemented to the varied inter-connected systems such as computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, or data.
The digital safety tool is tremendously flexible and possessed by distinct industries and of various designs or types. Various devices such as navigation apps, game apps, and social apps always have access to the internet, like our desktops, mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and others. Similar to that, even if you are pursuing a store or listening to music, there is a probability that you are engaging in the environment utilizing the necessities of cybersecurity’s modern definitions.
Contemporary, cyber security jobs contain the digital defense of information or data. Typically, it includes information storage protection, identification of intrusion, and response to cyber-attacks that seek to steal personal information. The scope of cyber security is huge and the niche of cyber security to digitally instantly raises concern. In India, cyber crimes are covered by the Information Technology Act, 2000, and Indian Penal Code, 1860 to prevent cyber crimes. The primary one takes care of issues associated with cyber crimes and electronic commerce, while the latter one, provides an outline and definition, including punishments, which we will discuss later in the blog.
It is to be noted that, cybersecurity encompasses –
1. Network Security
Primarily, cyber security emphasizes on data storage and transfer, while the network is much broader. As its name defines it, in general, network security includes the defense, maintenance, and recovery of networks. It contains cyber security as a defensive way to protect all network users from digital threats, even if a provided cyber attacker pertains more purposes than mere conservation of data exploitation.
With the objective to conserve the integrity, safety, and sustainability of network users, the professionals operating the same must emphasize on securing connection privacy to prevent cyber security.
The network security services also include anti-virus software, malware detection tools, firewall upgrades, virtual private networks (VPNs), and other security programs. As mentioned, the terms cyber security and network security are often used interchangeably, which often cover similar bases and deviate at intersections where data storage and data tracking need to overlap.
2. Information Security
Several commercial workplaces use synchronized facets of day-by-day operations. It handles user login, schedule management tools, project software, and telecommunication, among others.
It conserves sensitive information from unpermitted activities containing inspection, modification, recording, and other disruption or destruction. The objective of information technology is to ensure the safety and privacy of significant data such as details of a customer account, financial data, or intellectual property.
3. Operational Security
Operational security is also known as procedural security, which is referred to as a risk of managing processes to view the activity from the perspective of an adversary with the objective to conserve sensitive information from attackers. It includes the below-mentioned steps, as follows –
- Identification of sensitive data: Identify the sensitive data containing product research, intellectual property, financial statements, customer information, and employee information; this will be the data one will require to protect resources.
- Identification of potential threats: For every category of sensitive information, one must identify the potential threats. It is to be noted that, while you look for potential third-party risks, also watch out for internal threats.
- Analyzation of security holes and other vulnerabilities: One must access their information and means of safeguarding and determine the loopholes or other weaknesses associated with security.
- Enhance the level of security with respect to each vulnerability: Rank the distinct vulnerabilities based on the likelihood of attacks, the extent of damage, and the duration of recovery from the same.


What Are the Different Types of Cybersecurity?
In this section, we will highlight the different types of cyber security. Cyber security pertains to a wide field possessing distinct disciplines, which mainly can be characterized as follows –

a. Network Security
Major cyberattacks take place over a network and in order to ensure network security, network security solutions need to be utilized which are designed primarily to identify and block such attacks. Moreover, these solutions include data and access controls like Data Loss Prevention (DLP), IAM (Identity Access Management), NAC (Network Access Control), and NGFW (Next-Generation Firewall) application controls with the motto to enforce safe web use policies.
Besides this, in order to ensure multi-layered network protection, advanced technologies such as IPS (Intrusion Prevention System), NGAV (Next-Gen Antivirus), Sandboxing, and CDR (Content Disarm and Reconstruction) are utilized. However, this won’t be enough to prevent such attacks, therefore, network analytics, threat hunting, and automated Security Orchestration and Response (SOAR) must be used.
b. Cloud Security
Multi-National Companies (MNCs), large organizations, firms, and even startups are constantly adopting cloud computing, which makes cloud security a major priority considering that it engages in data storage, software information, networking, analytics, and intelligence over the internet with the sole objective to provide instant innovation, flexible resources and economies of scale.
Considering the threat to cloud security could result in a breach of security, therefore, it is significant to obtain a cloud security strategy containing cyber security solutions, controls, policies, and services that allow you to protect the entire cloud deployment against such attacks.
c. IoT Security
The full form of IoT is, the “Internet of Things”, which offers several productivity benefits to an organization, however, the same device tends to introduce the same organization to potential cyber security threats which result in breaches of vulnerable devices inadvertently connected to the internet. IoT security preserves devices from discovering and classification of connected devices, including automatic segmentation to administer network activities and utilizing IPS as a patch (virtual) in order to restrict the exploitation of vulnerable IoT devices.

a. Application Security
Like any other activities mentioned here, web applications are also connected to the internet which again impose threat due to flaws in application such as injection, broken authentication, misconfiguration, and cross-site scripting.
Application security is an appropriate way to prevent bot attacks and malicious interactions with APIs and web applications.
b. Mobile Security
Mobile security is often overlooked which allows access to corporate data, including exposing businesses to threats through malicious applications (apps), phishing, instant messaging attacks, and phone mirroring to name a few. Mobile security preserves such attacks and prevents operating systems and devices from such attacks.
c. Zero Trust
This traditional security model is a perimeter-emphasized model, which builds walls around the valuable assets of the organization. On the contrary, this imposes distinct issues like imposing possible inside threats and instant dissolution of the perimeter of the network. This security focuses on a granular approach in order to ensure security, including protecting individual resources by a combination of micro-segmentation, observing and enforcement of role-based access controls.
d. Endpoint Security
As mentioned earlier, the zero trust security model stipulates the creation of micro-segments around data segments wherever they might be. A way to prevent this is by using endpoint security. Endpoint security allows firms, organizations, and companies to preserve end users using devices like laptops, mobile phones, tablets, smartwatches, and desktops with data and network security controls, advanced threat prevention such as anti-phishing and anti-ransomware, and technologies.
In this section, we have understood the types of cyber security; now let’s move to the importance of cyber security to establish a better understanding of preventing cyberattacks since with the introduction of technologies, our vulnerability towards cyberattacks is constantly increasing.
The importance of cyber security differs based on the users or who is utilizing the technologies, it could be a student, business or organization, or banking sector, among others.
What Are the Distinct Importance of Cyber Security?
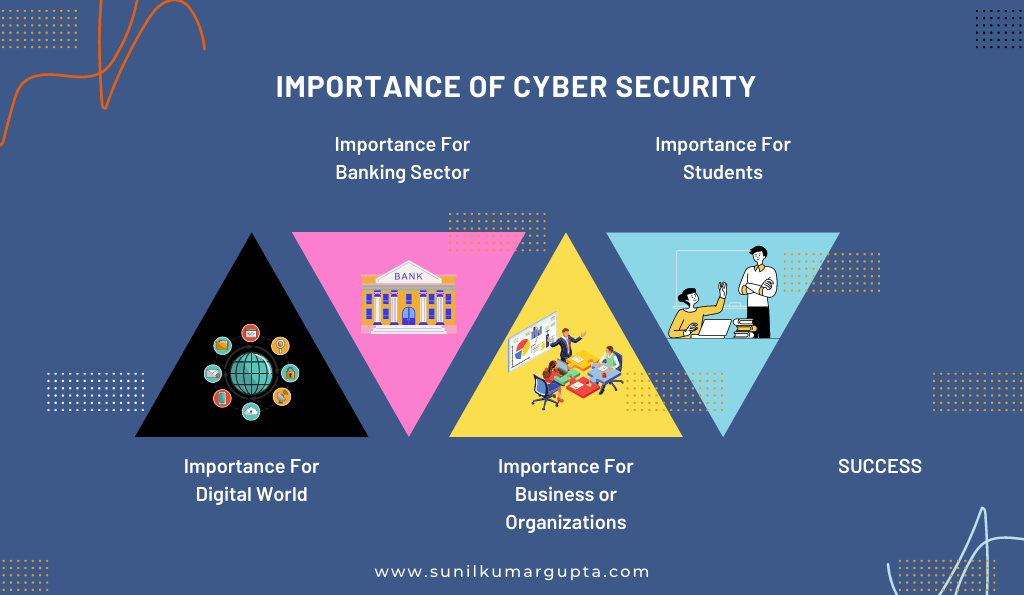
1. Importance For Digital World
Cybersecurity imposes significant threats to the digital world, especially, when the world is connected with each other digitally. For instance, in 2017 breach of Equifax exposed the data of over 145 million users, while in 2018 the breach of Marriot exposed the data (personal information) of 800 million individuals.
Such breaches of personal data or information had significantly affected the companies financially, most significantly resulting in losing customers. Hereto, cyber security is important to preserve businesses and persons from probable threatening consequences of data or security breaches.
2. Importance For Banking Sector
The banking sector is the backbone of any sector since a breach of the banking sector of an economy would result in a breach of names, emails, addresses, phone numbers, and other personal information, which further allows access to account information, containing account numbers and balances of customers.
Therefore, such breaches permit the hacker to access an abundance of sensitive data breaches, which could be the reason for fraud and malicious purposes.
3. Importance For Business or Organizations
The importance of cyber security for businesses or organizations allows hackers to access the data or personal information of customers or clients, which could also include information or details of credit or debit cards. This also results in businesses or organizations paying millions or billions to hackers.
4. Importance For Students
Cybersecurity is significant for students as well, which allows hackers to access their bank details and credit or debit card information, including access to their Social Security numbers.
With an understanding of the importance of cyber security, let head on to the features of cyber security in the next section.
What Are the Features of Cyber Security, One Should Know?
The entire world is interconnected with the internet, which has significantly enhanced during the pandemic through the usage of web applications or other websites. Despite bringing the entire world close, this has also presented an opportunity for cybercriminals to breach into our systems or mobiles. Considering the level of harm it can cause for an individual or organization or firm, everyone must immediately attain more knowledge with respect to the understanding of features of cyber security. An adequate understanding of the features of cyber security could be the primary step toward establishing a defense against such breaches and attacks.
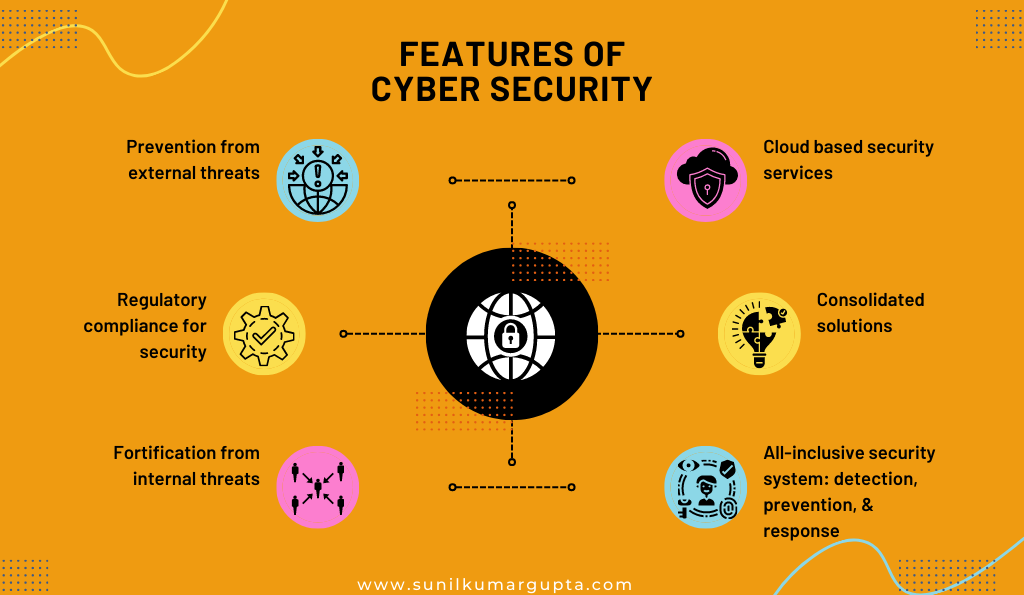
1. Prevention from external threats
External sources are causes for cyberattacks or breaches through phishing, denial of services, endangered web applications, and hostile email attachments, among others. Hereto, such security applications attached to respective systems constantly monitor or prevent these external threats.
2. Regulatory compliance for security
Information security is significant for any organization or firm, be it the healthcare sector or banking sector, or finance sector. Considering that, all the organizations or firms pertain to an eccentric set of standards, practices, regulations, and compliance with respect to data or information collected by them.
Regulatory compliance is basically ensuring conformance with compliance requirements to laws, specifications, and guidelines processes associated with the business.
3. Fortification from internal threats
Prevention from internal threats is as much as essential as ensuring preservation from external threats since both inflict threats on the organization or firm. The primary reason for triggering internal threats is misconfiguration, employee mistakes, faulty choices of employees, or bad actors.
Although, a definitive security system and a cybersecurity team attenuate these threats or attacks from organizations or firms.
4. Cloud-based security services
The cloud-based security services refer to the backend brain security systems which utilize a wide range of tools with the objective to ensure proper analytics and intelligence threat. Such services pertain a monitoring security endpoints and pervade machine learning models with the objective to ameliorate the scanning for all-inclusive objectives.
5. Consolidated solutions
Cybersecurity solutions should provide an absolute panacea to preserve the system of organizations or firms from the wide range of threats. In order to do so, the concerned security experts must know when and how to ensure complete utilization of anti-spam, anti-virus, anti-malware, content filters, and wireless security, among others.
This comprehensive protection or solution tends to preserve the system from such threats or attacks without compromising the confidentiality and security of data and enterprises.
6. All-inclusive security system: detection, prevention, & response
A wide range of security threats or cyber-attacks can be prevented or blocked by ensuring timely detection or tracking of the same. In order to do so, appropriate platforms are used that tracks such attacks and spontaneously send alert and response to them. The tools such as hardware and software firewalls, network analyzers, SSL or TLS proxy servers, and other web applications or apps or platforms are used.
Cybersecurity Security Awareness & Indian Economy
The Internet had brought a wave of transformation in everyone’s life by altering the way of communicating, sharing updates, playing games, shopping, and even making friends. The internet is affecting every part of our daily life.
Considering its effect on our daily lives and every sector of the economy, it is significant to attain the proper education regarding the proclamation of information with the objective to prevent cyberattacks or crimes, including reenacting that students play a crucial role in creating an ecosystem of cyber security with the motto to restrict cyber-attacks or crimes.
Cyberspace interconnects us globally and keeping in the view that its usage is constantly expanding, the rate of cybercrimes, especially against children and women are rising such as cyberstalking, cyberbullying, cyber harassment, child pornography, and rape content, among others. With the objective to create a safe and sound cyber ecosystem, it is essential to follow cyber-safe practices.
With that, let’s move on to cyber crimes laws in India –
a. Information Technology Act, 2000 (IT Act)
The IT Act enacts cyber laws in order to regulate electronic means of communication, and trade, including commerce to prevent computer crimes. The overview of the act is defined as –
“An Act to provide legal recognition for transactions carried out by means of electronic data interchange and other means of electronic communication, commonly referred to as “electronic commerce”, which involve the use of alternatives to paper-based methods of communication and storage of information, to facilitate electronic filing of documents with the Government agencies and further to amend the Indian Penal Code, the Indian Evidence Act, 1872, the Bankers’ Books Evidence Act, 1891 and the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.“
Penalty & Compensation
- Section 43 of the IT Act
The provisions under section 43 of the Information Technology Act, 2000 defines as –
If any person without the permission of the owner or any other person who is in charge of a computer, computer system, or computer network-
“(i) accesses such computer, computer system or computer network or computer resource; (ii) downloads, copies or computer system or computer network or computer resource; (ii) downloads, copies or extracts any data, computer data-base or information; (iii) introduces or causes to be introduced any computer contaminant or computer virus; (iv) damages or causes to be damaged any computer, computer system or computer network data, computer database or any other programmes; (v) disrupts or causes disruption; (vi) denies or causes the denial of access to any person authorised to access; (vii) provides any assistance to any person to facilitate access in contravention of the provisions of this Act; (viii) charges the services availed of by a person to the account of another person by tampering with or manipulating any computer, computer system or computer network; destroys, deletes or alters any information residing in a computer resource or diminishes its value or utility or affects it injuriously by any means; (x) steal, conceals, destroys or alters or causes any person to steal, conceal, destroy or alter any computer source code with intention to cause damage; he shall be liable to pay damages by way of compensation to the person so affected.“
It simply signifies that if an individual commits cybercrimes like computer damage to a victim without the consent of the same. Then the owner of the computer is entitled to a refund of the entire damage. While section 66 is applicable to any conduct provided in Section 43 which is considered to be dishonest and fraudulent the cyber criminal is punishable with imprisonment of up to 3 years or with a fine which might extend up to rupees five lahks, or both.
While section 66 is applicable to any conduct provided in Section 43 which is considered to be dishonest and fraudulent the cyber criminal is punishable with imprisonment of up to 3 years or with a fine which might extend up to rupees five lahks, or both.
2. Further Extension of Section 66
Section 66B is defined punishment for deceitful stealing of computer resources or communication devices, it is defined as –
“Whoever dishonestly receive or retains any stolen computer resource or communication device knowing or having reason to believe the same to be stolen computer resource or communication device, shall be punished with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to three years or with fine which may extend to rupees one lakh or with both.“
Section 66C, includes information associated with punishment related to identity theft such as using an electronic signature, password, or any other unique identification feature fraudulently or dishonestly, which describes punishment as –
“Whoever, fraudulently or dishonestly make use of the electronic signature, password or any other unique identification feature of any other person, shall be punished with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to three years and shall also be liable to fine with may extend to rupees one lakh.“
Section 66D, this section involves information associated with punishment for cheating by personation by using computer resources, which is defined as –
“Whoever, by means for any communication device or computer resource cheats by personating, shall be punished with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to three years and shall also be liable to fine which may extend to one lakh rupees.”
Section 66E, this section of the information technology act includes information related to punishment associated with privacy violations such as taking pictures of private areas, and publishing/ transmitting these images without the consent of the concerned individual. If found guilty, the criminal would be punished with imprisonment of up to 3 years or a fine, which can extend up to rupees two lakh or both. Section 66F, the section 66F of the Information Technology Act defines punishment associated with cyber terrorism, be it to threaten the unity, integrity, security, or sovereignty of India or to strike terror in the people. In such cases, the cybercriminal would be punished with imprisonment, which could extend to life imprisonment
3. Section 67
Section 67 includes punishment associated with publishing or transmitting obscene material in electronic form, as –
“Whoever publishes or transmits or causes to be published or transmitted in the electronic form, any material which is lascivious or appeals to the prurient interest or if its effect is such as to tend to deprave and corrupt persons who are likely, having regard to all relevant circumstances, to read, see or hear the matter contained or embodied in it, shall be punished on first conviction with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to three years and with fine which may extend to five lakh rupees and in the event of second or subsequent conviction with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to five years and also with fine which may extend to ten lakh rupees.”
b. Information Technology Rules (IT Rules)
The different aspects of data collection, transmission, and processing are covered under this rule as –
It includes details related to sensitive information personal details withheld by entities such as –
- Password;
- Financial information such as Bank account or credit card or debit card or other payment instrument details ;
- Physical, physiological, and mental health conditions;
- Sexual orientation;
- Medical records and history;
- Biometric information;
- Any detail relating to the above clauses as provided to the body corporate for providing service;
- Any of the information received under the above clauses by the body corporate for processing, stored, or processed under lawful contract or otherwise
This section defines a set of rules, procedures, practices, and sensitive personal data or information which needs to be complied with. Moreover, an audit will be duly conducted once a year or as required.
- The Information Technology (Guidelines for Intermediaries and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021
The Information Technology (Guidelines for Intermediaries and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021 help in maintaining the safety related to the online safety of data of users, which administer the role of intermediaries or social media intermediaries with the objective to restrict the data transmission on the internet.
It includes guidelines for the cyber cafes to be complied with, and it includes registration of cyber café to generate unique identification numbers, identification of users, and management of physical layout and computer resources, among others.
This Act includes information related to the electronic service delivery of certain services like applications, certificates, and licenses, by electronic means. It specifically emphasizes on the services provided by the government signifying compliance requirements related to the Creation of a repository of electronically signed electronic records by Government Authorities, Procedures for making changes in a repository of electronically signed electronic records, among others.
This Act includes rules related to distinct CERT-In Rules as per Rule 12 of the CERT-In Rules, providing a 24-hour response help desk. This help desk is operational 24 hours to report the cyber security incidents of persons, organizations, and companies, in case they experience cyber attacks.
c. Indian Penal Code, 1860 (IPC)
The Indian Penal Code, 1860 includes mentioned sections to prevent cyber crimes –
1. Section 292
This section excises control over punishment related to the publishing or transmission of obscene material or sexually explicit material digitally or electronically. In such case, a fine of 2000 or imprisonment of up to 2 years would be imposed.
2. Section 354C
It defines punishment related to taking or publishing images of the private parts of a woman, including actions. The section 354C is defined as –
“Any man who watches, or captures the image of a woman engaging in a private act in circumstances where she would usually have the expectation of not being observed either by the perpetrator or by any other person at the behest of the perpetrator or disseminates such image shall be punished on first conviction with imprisonment of either description for a term which shall not be less than one year, but which may extend to three years, and shall also be liable to fine, and be punished on a second or subsequent conviction, with imprisonment of either description for a term which shall not be less than three years, but which may extend to seven years, and shall also be liable to fine.“
3. Section 354D
It includes provisions associated with cyber stalking are included in this section, including tracking, emailing, including attempts to contact her through digital means or electronically. It is defined as –
“Whoever commits the offence of stalking shall be punished on first conviction with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to three years and shall also be liable to fine; and be punished on a second or subsequent conviction with imprisonment or either description for a term which shall not be less than three years but which may extend to seven years and with fine which shall not be less than one lakh rupees:
Provided that the count may, for adequate and special reasons to be mentioned in the judgement, impose a sentence of lesser period of imprisonment than specified minimum imprisonment.“
4. Section 420
This section includes punishments related to cheating and dishonesty associated with property delivery, which imposes imprisonment of up to 7 years along with fine for crimes such as fake websites or online or cyber frauds.
5. Section 463
Section 463 involves a punishment of 7 years or a fine, or both for the creation of false documents or false electronic records or part of a document or electronic record.
6. Section 465
This section is defined as –
“Whoever commits forgery shall be punished with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to two years, or with fine, or with both.”
d. Companies Act, 2013
The Companies Act 2013 includes the daily obligations to be complied with by the corporate stakeholders. Each provision associated with the Information Technology Act, 2000 related to electronic records involving the manner and format of electronic recording, as far as it is in variance with the concerned Act would be applicable to records of the electronic form provided under Section 39
Considering that, the Indian government has taken certain initiatives to prevent cyber-attacks or crimes as follows –
Cyber Crime Awareness Booklet on Cyber Security Awareness
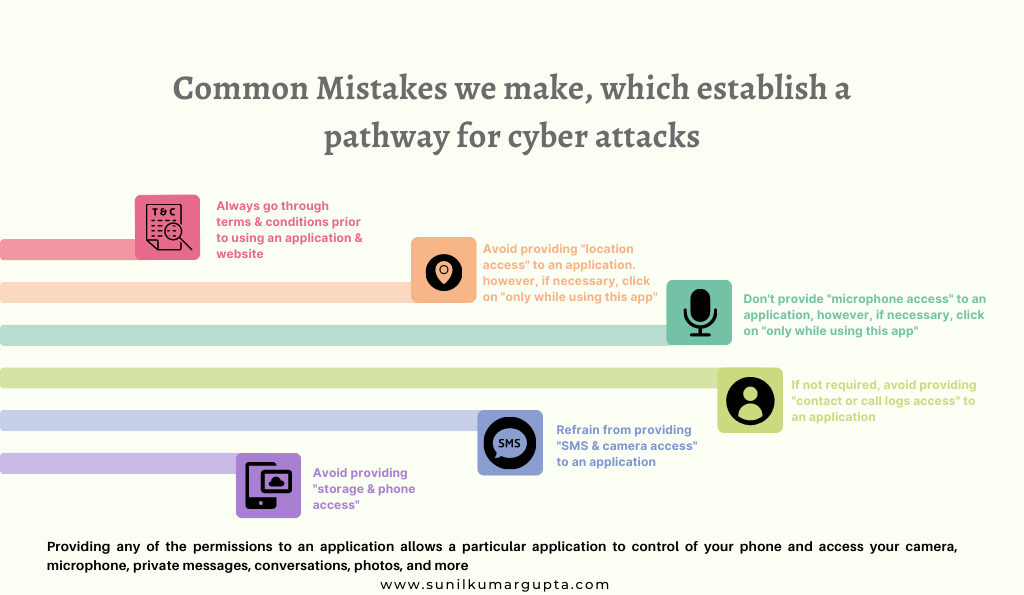
Under Cyber Security Awareness, the tips for preventing cybercrime are –
- To keep your devices or mobile phones updated with advanced or updated safety patches.
- Use the appropriate security software (latest version) to preserve your system or devices.
- Always use or download the software or applications from trusted or known sources, and restrict from using pirated software on your system or devices.
- Protect your devices or mobile phones with strong PIN codes or passwords and do not share the same with anyone.
- Restrict sharing your net banking password, One Time Password (OTP), ATM/ mobile banking PIN, or CVV, among others with anyone, even if someone claims to be an employee of the bank.
- Ensure to change the default admin password of the wifi router to a strong one and keep your wireless network encrypted.
- Be cautious when using public wifi, including avoiding entering your personal and professional information or details while using these networks.
- Use the virtual keyword to access net banking services on public computers and be sure to log out from the same after completion of the online transaction. Moreover, ensure to delete the browser history.
- Be certain to scan all the email attachments from viruses prior to opening the emails, including ignoring downloading from untrusted emails.
- Be cautious while sharing your identity proof, especially the one which identifies your personal or company identity.
- Keep the IMEI code of your mobile in a safe place that can be the only access to you, an operator could blacklist or block or phone using your IMEI code, if your mobile phone is stolen.
- Prior to entering your ATM PIN, observe your surrounding and the people around you.
- Engaged in a detailed discussion of safe internet practices with your family and friends, including motivating them to follow the same in order to prevent cybercrimes or attacks.
- Avoid sharing bank details or card details on e-wallets it enhances the possibility of theft or fraud due to a breach of security.
- Contact the concerned authorities instantly if you think your safety is compromised.
Cyber Hygiene for cyberspace
Under the cyber hygiene initiative of the government, the Indian government has introduced some dos and don’ts to be followed in cyberspace emphasizing on different platforms.
Cyberspace is a complex and dynamic environment of interactions among people, software, and services supported by the worldwide distribution of Information and Communications Technology (ICT) devices and networks. The exponential increase in the number of internet users in India clubbed with rapidly evolving technologies has brought in its own unique challenges. Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) under the Cyber & Information Security (CIS) Division of the Ministry of Home Affairs has prepared this manual to disseminate Cyber Hygiene Best Practices for the benefit of Industrial Bodies/General Public/Government Officials. This should not be considered an exhaustive list of precautions for Cyber Hygiene but baseline precautions that are to be taken.
- Computer safety tips

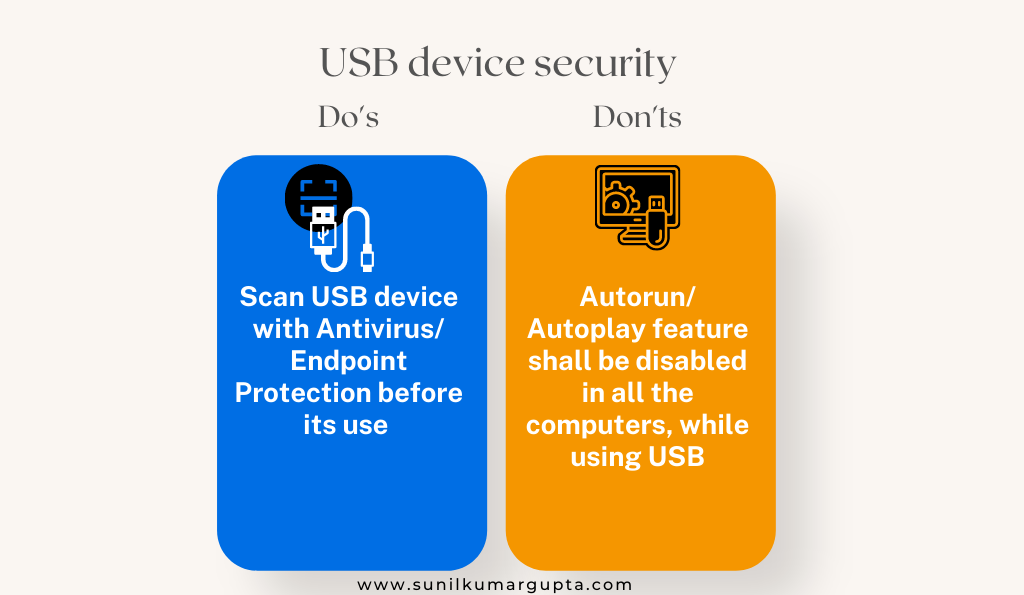
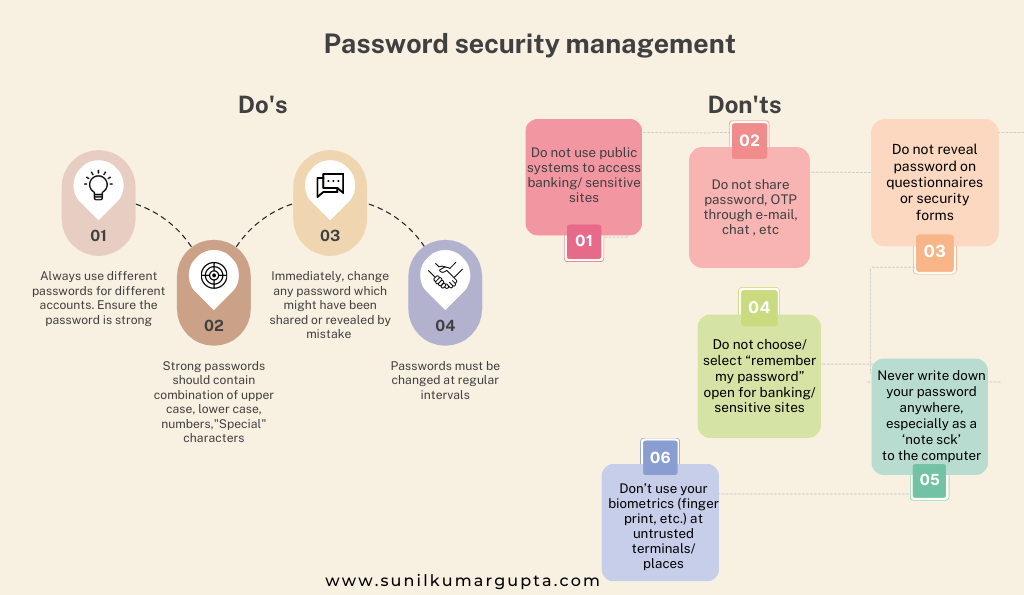
- Password security management
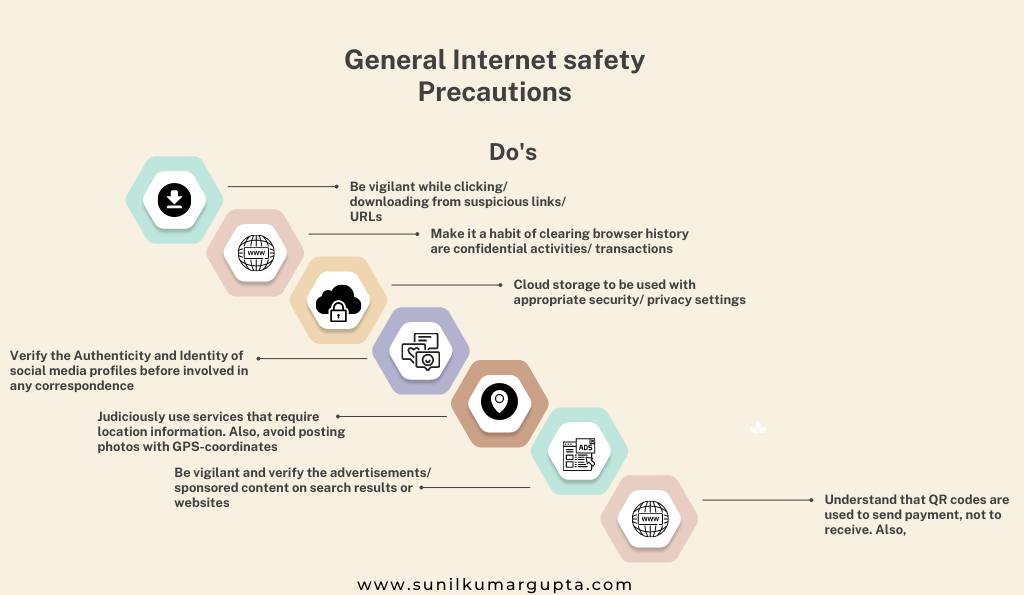
- General Internet Safety Precautions

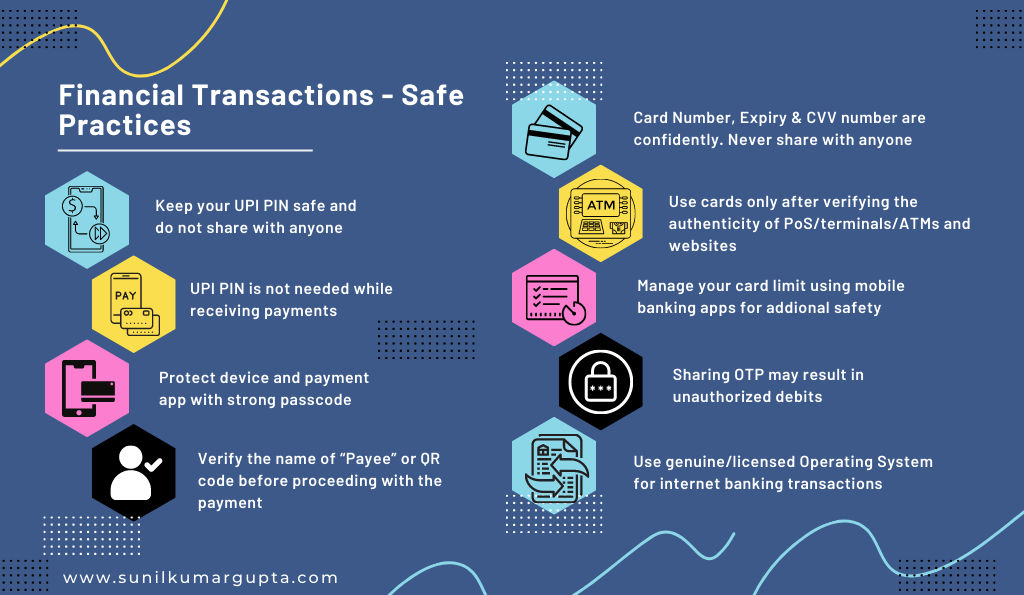
- Financial Transactions – Safe Practices
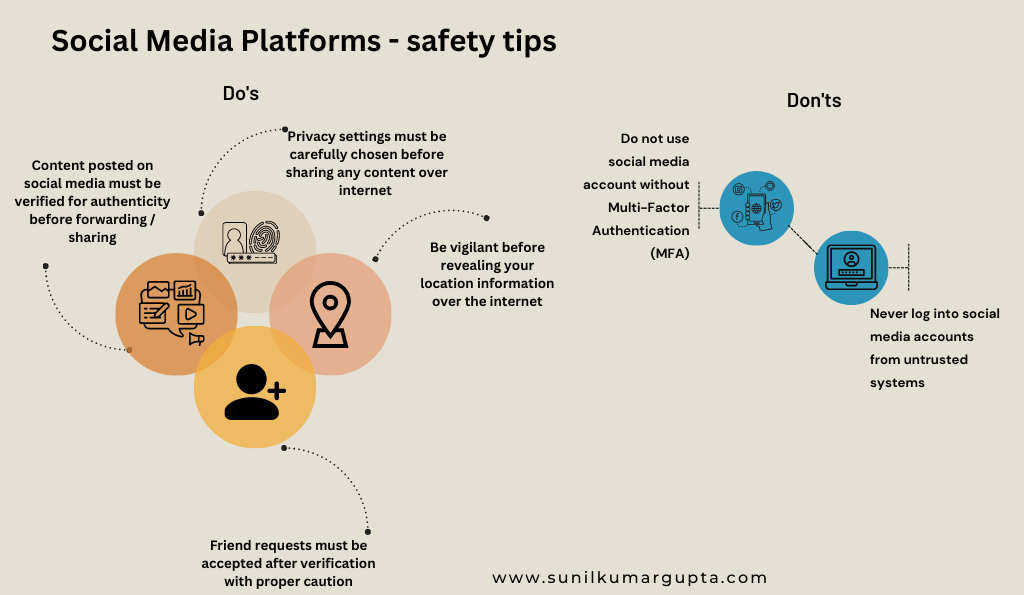
- Social Media Platforms – Safety Tips
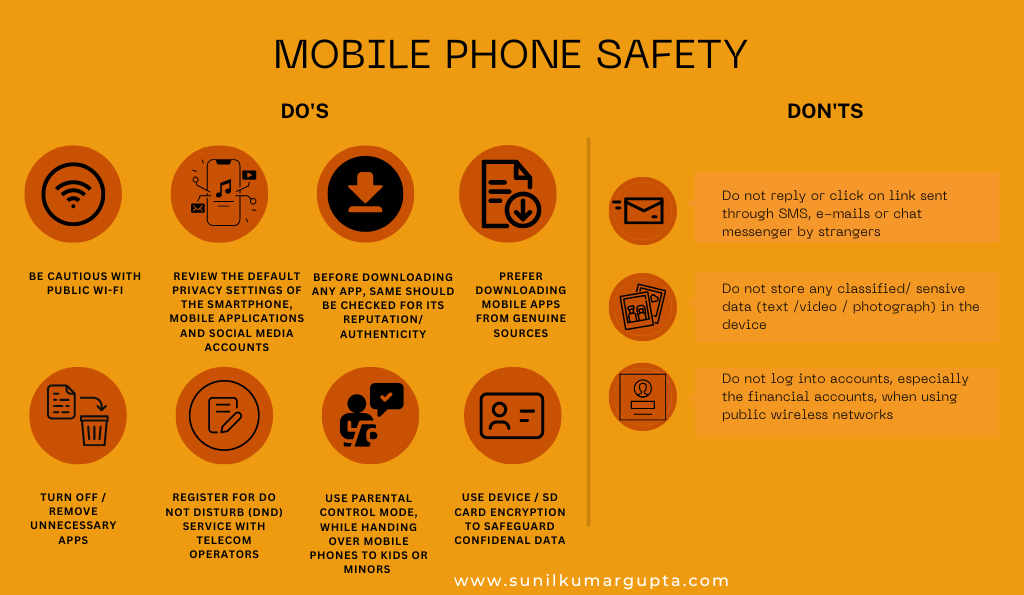
- Mobile Phone Safety
- Malware and E-mail Security Practices

Above mentioned is how the Indian government is promoting cyber security, emphasizing email security practices in social media. However, in the next section, we will describe various steps taken by the government to promote cyber security, especially for students.
Describe Various Steps Taken by the Government to Promote Cyber Security For Students
The cyber-attacks are becoming highly challenging as well as sophisticated nowadays, especially through the usage of social media platforms, emails, chatrooms, and websites, among others.
Email spoofing (a technique used in spam and phishing attacks to trick users into thinking a message came from a trusted person or entity), cyberbullying (using an electronic means of communication to bully an individual), job frauds, banking frauds, identity theft, among others have increased with the time, especially after covid, as it has given a kick start to a new era of digitalization. Though, covid-19 has pushed distinct sectors of the economy to work digitally, which certainly contributes to the growth of the economy, while on the other hand, the same can be seen as a significant cause of the increase in cybercrimes.
Let’s commence with how the Indian government is taking initiatives to prevent cyberbullying is often referred to as cyber harassment under which electronic means are used to bully or harass an individual –

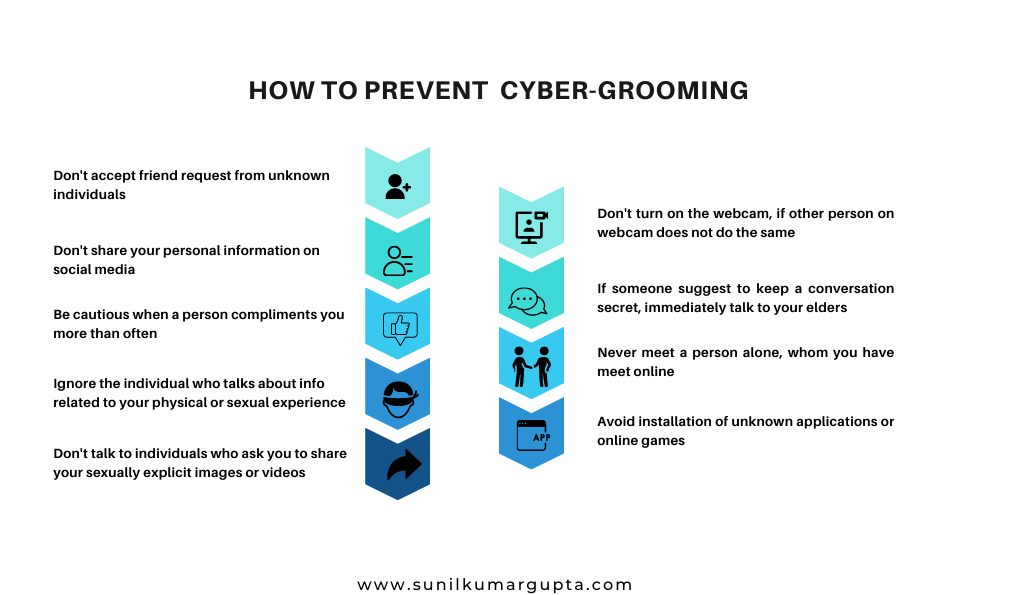
With the understanding of it, let’s move on to how the Indian government is helping in the prevention of cyber-grooming, which is referred to a situation in which an individual, often an adult befriends a child online and builds an emotional connection with the intention of sexual abuse, sexual exploitation or trafficking –
Besides social media, the Indian government, like any other economy is taking appropriate initiatives to prevent cybercrime. Recently, the Central government introduced and launched “Cyberdost” (February 2019) – a Twitter handle that is responsible for creating awareness regarding cybersecurity in order to create awareness regarding the same, @cyberdost has tweeted 1066+ tweets containing videos, images, and creatives providing general safety tips to prevent cybercrimes or attacks.
Besides this, we have to dive a little deep into how the Indian government is promoting cyber security, then we would like to highlight that the Indian government has actively engaged in –
- Radio campaigns
- SMS sharing with respect to creating awareness against cybercrimes
- Publicly publishing videos, images, and creatives providing general safety tips to prevent cybercrimes or attacks
- Publication of Handbook emphasizing “cyber safety of adolescents or children”
- Publication of Best security practices to reduce or prevent cybercrimes against government bodies
- Cyber safety and security awareness are being organized through C-DAC along with Police Department of various states
All such measures have been taken keeping the mission of preventing cybercrime.
Conclusion
Just like the entire world, the Indian economy is also considerate regarding the problems introduced by cyber security. This blog highlighted how the Indian government is promoting cyber security, we would like to emphasize that, be it issuing measures, tips, and practices to be followed to prevent cybercrimes with respective departments or ministries, the Indian government has formed the relevant policies and measures to prevent such hideous actions, which does not only cause loss of money but affects the life of a person.
Besides this, the Indian government has successfully introduced and implemented Acts and schemes to prevent cyber security attacks or crimes, such as Information Technology Act, 2000 (IT Act), Indian Penal Code, 1860, and Information Technology Rules (IT Rules), among others. Also, considering the risk imposed by cyber crimes, the Indian government has appropriately included daily obligations to be complied with by the corporate stakeholders to restrict the same issue. The Indian government has dedicated most of its resources not only to making India a developed country, however, also to preventing the breach of information through incorporating legal and technological advances without compromising digitalization.
Written & Compiled by CA Sunil Kumar Gupta
Founder Chairman, SARC Associates
